Ovary
Every woman is endowed with two ovaries on either side of the uterus. The ovaries secrete the female hormones and also bear the eggs.
Functional
Details
The ovaries are a pair of small, almond-shaped organs in the female reproductive system. They are present in the female pelvis on the right and left of the uterus. They are responsible for releasing an egg on a monthly basis during a woman’s reproductive years. One other important function of the ovaries is to produce the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. These hormones are necessary for a woman’s menstrual cycle, pregnancy, if present, body shape, bone health and overall health.
Functional Ovarian Cysts
Before the egg is released from the ovary, it forms a small fluid-filled sac called a follicle. If the follicle does not break open and the fluid is not released, a follicular ovarian cyst may develop. If the follicle reseals after it bursts and the fluid re-accumulates, a corpus luteum cyst will form. Bleeding inside the follicle results in a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst. These types of cysts are called functional cysts, as they may develop monthly during the normal function of the ovary. Functional cysts are the most common types of ovarian cysts, and they usually resolve within one to two months.
Benign Ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts that are not part of a menstrual cycle are known as ovarian tumors. Some tumors can be cystic or filled with fluid, some can be solid, and some can have both cystic and solid components. Ovarian tumors usually do not resolve and require surgical removal.
Parijatham Clinics & The Surgical Centre – Our specialists are rated as Best Ovarian Cyst Specialists based on thier more than 20 years of Experience in Laparoscopy and Gynaecological Surgery.
Best Ovarian Cyst Specialists

Reach out to the Best Ovarian Specialists in Hyderabad Now
Benign Ovarian Mass
- Dermoid Tumor – This tumor is also known as a Mature Cystic Teratoma and has both a cystic and solid component. It is filled with tissue from other parts of the body such as hair, teeth and fat. These tumors most commonly occur in teenage girls and young women.
- Mucinous Cystadenoma – This is an ovarian cyst that contains mucous material. It is the most common benign ovarian tumor and can grow very large.
- Serous Cystadenoma – This is an ovarian cyst that contains clear yellow fluid.
- Endometrioma – This is also known as chocolate cyst. It is filled with endometriotic fluid, which has a thick brown consistency.
- Fibroma – This is a solid ovarian tumor resembling a fibroid. It can often be mistaken for a pedunculated fibroid on the ultrasound or MRI.
Pelvic Mass
A pelvic mass is a general term for any growth or tumor on the ovary or in the pelvis. A pelvic mass from ovary can be cystic (cystadenoma), solid (fibroma), or both (dermoid). A pelvic mass can be benign or malignant.
Do remember that pelvic masses can arise from other structures in the pelvis like intestines, soft tissue etc.
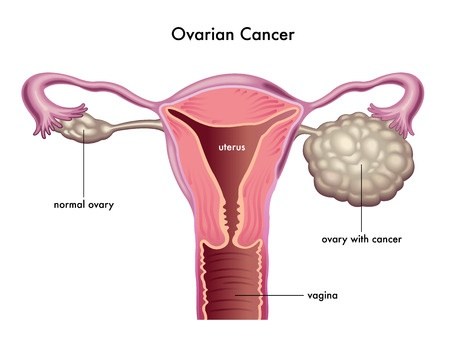
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancers also present as masses from the ovaries. Most common form ovarian cancer is commonly seen in women after 50 years. But germ cell tumors occur in young girls and women under 30 years.
These tumors present as solid masses causing abdominal discomfort and sometimes in an emergency due to torsion or rupture.
Differentiation from benign non malignant masses of the ovary is based on radiology, blood tests and sometimes only after surgery. It is important to get evaluated by Ovarian Cyst Specialists
Blood markers like Ca125, Bhcg and AFP etc are commonly done when ovarian masses look suspicious.
WHAT ARE COMMON SYMPTOMS THAT YOU MIGHT HAVE WITH AN OVARIAN CYST OR PELVIC MASS?
In most cases, ovarian cysts are small, harmless and produce no symptoms. In other cases, cysts may cause problems if they get larger, if they twist (ovarian torsion), or if they burst and cause internal bleeding. Immediate attention and treatment is then needed. If you have an ovarian cyst, you might experience any of the following symptoms:
- Menstrual irregularities or abnormal bleeding
- Dull ache in your lower back or thighs
- Pelvic pain shortly before or after the beginning of your menstrual cycle
- Pelvic pain with intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Fullness or heaviness in your abdomen
- Nausea, vomiting or bloating
- Pressure on your bowel or pain during bowel movements
- Difficulty emptying your bladder completely
It is always important to remember that some ovarian cysts may be cancerous. Although very rare in younger women during their reproductive years, the risk of ovarian cancer increases with age.
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE OVARIAN CYSTS?
Ultrasound: Examining an ovarian cyst via ultrasound will help determine proper diagnosis and management. Essentially, aspects examined include the shape (regular or irregular), the size, and the composition of the cyst. It is important to know whether a cyst is fluid-filled, solid or mixed. Fluid-filled cysts (commonly called simple cysts on an ultrasound) are not likely to be cancerous and most often require observation and close follow-up unless they are too large or causing disturbing symptoms. Those cysts that are solid or mixed (fluid-filled and solid) may require further evaluation to determine if cancer is present and most often require surgical treatment. These cysts are commonly called complex cysts on the ultrasound.
- MRI: Usually reserved for solid tumors.
- Blood tests: Pregnancy test, hormone levels and CA-125 may be necessary, depending on the characteristic of the cyst on the ultrasound.
WHAT DOES MY CA-125 RESULT MEAN?
CA-125 is a blood test that can be performed to rule out ovarian cancer. However, the results are often high in premenopausal women, because many other benign conditions can lead to an elevated CA-125 level. Endometriosis, fibroids, noncancerous ovarian cysts, infection, liver disease, and many other conditions can falsely elevate the value and give patients an unnecessary scare. The test is somewhat more effective in postmenopausal patients.
In some cases, observation may be all that is necessary, especially for small, functional cysts causing no symptoms. For women who require removal of ovarian cysts or removal of the ovaries, including women seeking prophylactic oophorectomy to reduce future cancer risk, Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery offers fast solutions and nearly painless recovery.
SURGICAL TREATMENT OPTIONS
Laparoscopy is very effective for cysts or masses involving the ovaries or fallopian tubes. Benign (non-cancerous) cysts of the ovary can usually be removed, while preserving the ovary. Extremely large masses or endometriomas may require removal of the entire ovary and fallopian tube. Patients seeking cancer prevention due to increased genetic risk factors will also require complete removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
A decision to remove an ovary is based on the patient’s age, the likelihood of cancer, and the safety of the procedure. Every effort is made to preserve ovaries for patients who desire fertility. However, patients with suspected cancers, with family or personal history of breast or ovarian cancer, or with prior histories of ovarian pain or scarring may need complete removal of the ovary at the time of surgery.
The size and type of cyst present determine if the ovary will need to be removed. A woman’s ovaries are only removed after a full discussion of this possibility before surgery, or if there is no way to remove a mass without significant blood loss or compromising safety during the procedure.
HOW ARE OVARIAN CYSTS OR PELVIC MASSES REMOVED?
Pelvic mass surgery can be performed laparoscopically, no matter the size. This includes ovarian cystectomy (ovarian cyst removal), or oophorectomy (removal of the entire ovary and cyst). During an oopherectomy, the fallopian tube is usually also removed during the procedure since it is adherent to the ovary and may cause further complications if left in place.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF LAPAROSCOPIC TREATMENT?
Since the vast majority of ovarian cysts and masses in premenopausal patients are benign, laparoscopy is a great option for many patients. Minimally invasive procedures allow patients to avoid large open incisions for the removal of their cysts, thereby decreasing hospital stays, recovery times, and pain. Postmenopausal patients with masses are also usually benign, with cancer rates ranging from five to 20 percent of all masses, depending on the study cited. Laparoscopy is of significant benefit for these patients as well, since it will prevent an open surgery, and recovery from open surgery can be increasingly difficult for older women.
Women who have laparoscopic cystectomy or oopherectomy are almost always discharged from the hospital the same day, with excellent pain control and rapid recovery. Most patients are back to work within seven days
WHAT IF MY OVARIAN MASS IS CANCEROUS?
If cancer is identified, a staging operation is performed during the same surgery. Staging means evaluating other areas such as lymph nodes to rule out metastasis, or spread of disease, that may require chemotherapy. Frozen section and staging with identification of cancer is helpful to both the surgeon and the patient. By having the section immediately reviewed and staging in the same surgery, the patient avoids having to undergo a second surgical procedure at a later date. Not only is laparoscopic surgery easier to recover from for all patients, but we find that our oncology patients feel better and stronger if chemotherapy is required, if they are not recovering from extensive open surgery as well. Occasionally, a patient with more extensive malignancy will require open surgery for complete removal of malignant masses, as indicated.
Our Advantage
The surgeons at Parijatham have a niche focus: techniques for GYN surgery that facilitate optimal care and rapid recovery. Because we are so focused on GYN surgery, and with additional expertise on gynaecological cancers, we are better prepared in case the ovarian mass is maligant!
Best Ovarian Cyst Surgery Specialist Centre in Hyderabad
Contact Us
Exclusive Gynaecology centre with senior Gyn Surgeon. Complete lab and diagnostic facilities!

